Radio-frequency Identification
Why RFID
- Faster handling with goods and the elimination of errors
- Collective automated object detection
- Increase of savings by reducing of incorrect deliveries
- Reduction of total costs
- Accurate inventory information, inventory management
- Protection against theft of goods
- Monitoring of work in production
- Additional refinement of information
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a technology that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency (RF) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal, or person. RFID is coming into increasing use in industry as an alternative to the bar code. The advantage of RFID is that it does not require direct contact or line-of-sight scanning.
There are several methods for uniquely identifying by using RFID, but the most common is to preserve the EPC code along with the serial number and other relevant information to enable recognition and traceability of a specific product.
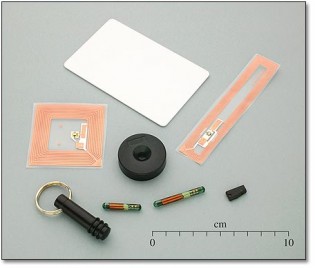
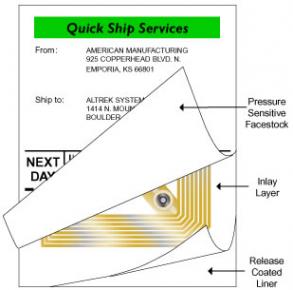
Whole information is stored on a microchip that is attached to an antenna and molded into the substrate. Together these components constitute the so-called RFID tag, which is capable of storing information to send to the reader. It converts the emitted radio waves received from the RFID tag into a form that can be further processed.
RFID tag may take the form of smart label - labels suitable for further printing sleeve or form various shapes, sizes and materials.
RFID tags
Types:
- read only
- write-once, read-many (WORM)
- read and write
There are also different types of transponders:
- Active transponders - these are systems with their own power supply (battery). Wide reading ranges are possible, mostly independent of the environment. Disadvantage is size and limited life.
- Passive transponders - these are systems that are only activated when they get close to a reader. Small size and inexpensive.
There are different types of RFID systems, the difference lies in the frequency they use:
- class 0 or 0+ or 1
- generation 1 (GEN 1) or 2 (GEN 2)
Pasive:


Active:



RFID vs bar codes
RFID technology has not occurred with the intent to replace barcodes, but extend the already established system to new opportunities and possibilities. In many applications it is therefore advantageous to use combinations of these two technologies - thus SmartLabel.
Differences:
- the possibility of updating the stored information (for read / write tags)
- no line of sight required
- multiplexed sensing at a time
- resistance to temperature, humidity and ambient influences and production processes and technologies
- much bigger than capacity of carried information
Advantages:
- reduction of errors
- transferability of media
- improved control of the flow of goods and logistics
- higher level of automation
- Digital access to information
- speed of obtaining information, the possibility of multiple reading
- mobility
- traceability to the level of individual product
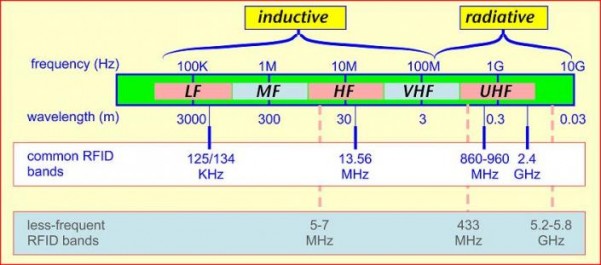
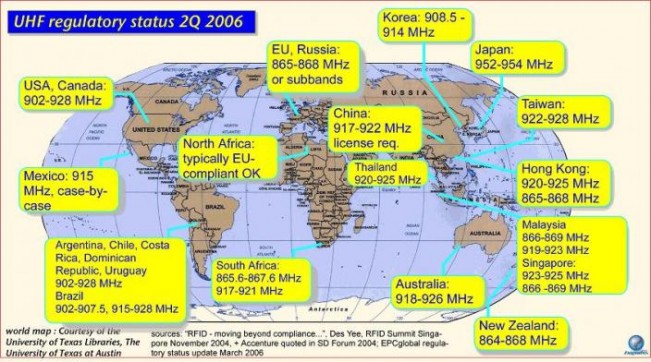
Frequency
The antenna uses radio frequency waves to transmit a signal that activates the transponder. When activated, the tag transmits data back to the antenna. The data is used to notify a programmable logic controller that an action should occur. The action could be as simple as raising an access gate or as complicated as interfacing with a database to carry out a monetary transaction. Low-frequency RFID systems (30 KHz to 500 KHz) have short transmission ranges (generally less than six feet). High-frequency RFID systems (850 MHz to 950 MHz and 2.4 GHz to 2.5 GHz) offer longer transmission ranges (more than 90 feet). In general, the higher the frequency, the more expensive the system.
Main fields of application
Possibilities of using RFID in any industry and any application are limited only by the available technology and the implementation.
Here is just a small list of common areas where RFID technology is used:
- transport and logistics
- retail
- health-care
- production (automobile industry, electro-technical, …)
- warehouse management
- evidence and property inventory
- packaging (generally cartons, boxes, crates, pallets)
News
We know our job and understand your needs. More than 30 years of experience in automatic identification.
Kontaktujte nás
This international sales marketing campaign was realized with the financial support of the South Moravian Region through the Project „Centre for International Trade“